Description
The file is a 32-bit Windows executable that contains BlackCat Ransomware, BlackCat, also known as Noberus or ALPHV, is a sophisticated ransomware family programmed in Rust and deployed as part of Ransomware as a Service (RaaS) operations on Windows, The ransomware can be configured to encrypt files using either AES or ChaCha20 algorithms, In addition, it can delete volume shadow copies, terminate processes and services, and halt virtual machines on ESXi servers, ALPHV also possesses self-propagation capabilities, enabling it to remotely execute itself on other hosts within the local network using PsExec, to execute, the ransomware requires an access token to decrypt its config, This indicates that the ransomware was deployed and activated using another file, However, since the access token wasn’t retrieved, dynamic analysis of the malware was not possible.
Analyzing ALPHV
The ransomware has never been submitted to VirusTotal, This could suggest that it is part of a targeted campaign
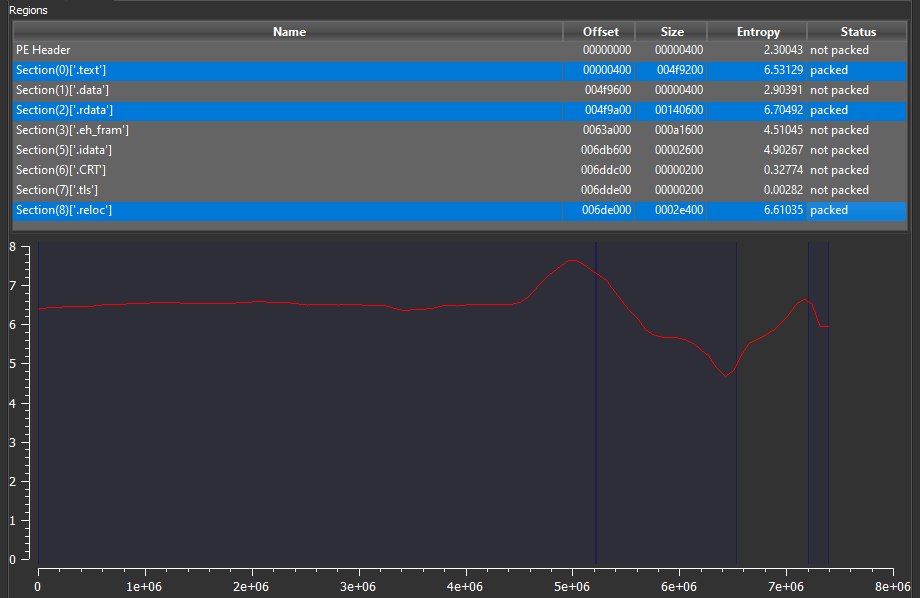
The ransomware TEXT and RDATA and RELOC sections are packed
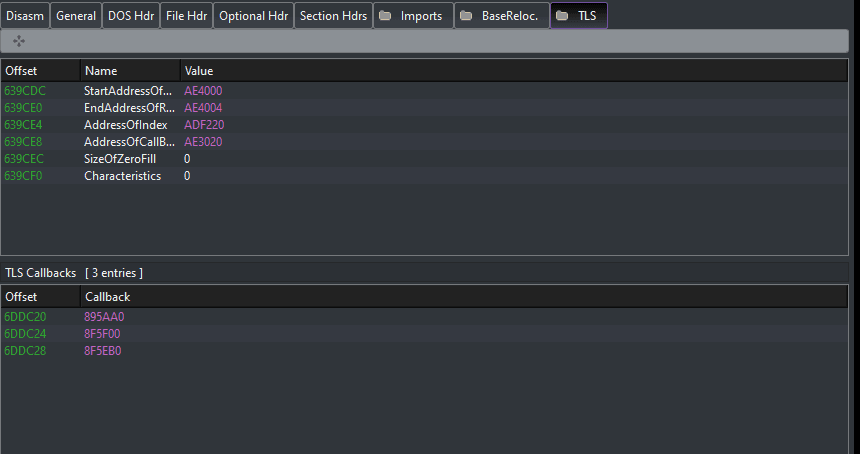
The ransomware uses three local thread storages to hide its main functions and evade detection, complicating its code for analysis or debugging
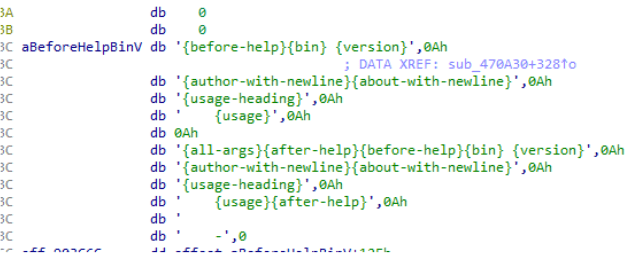
when ransomware is executed the output indicates its support command line arguments, which is a feature added by ALPHVto simplify its use in the Ransomware as a Service (RaaS) model.

The string located in its binary reaffirms the aforementioned information.
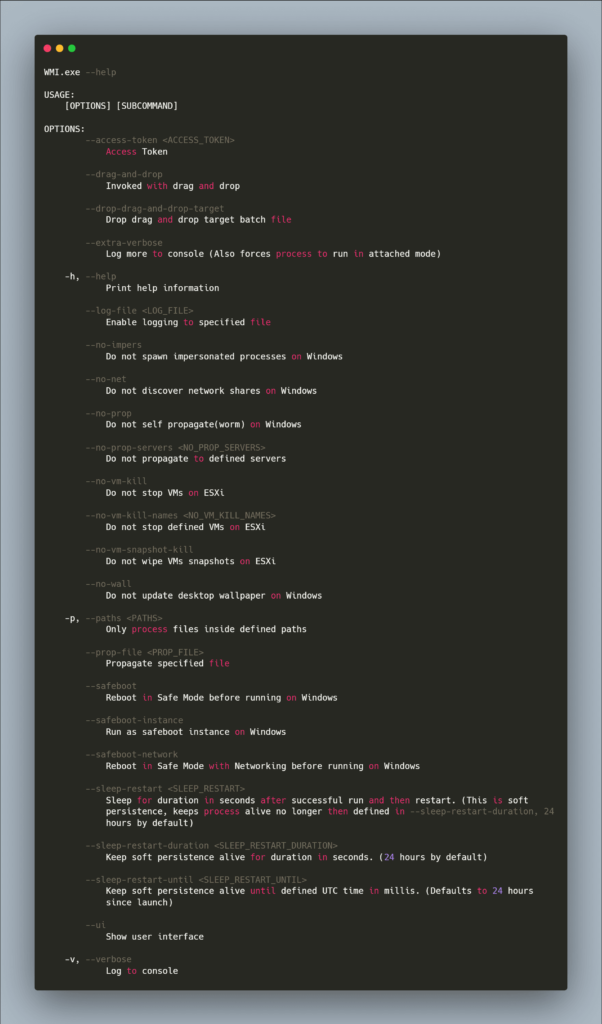
Utilizing the command line with the binary provides an output containing all available options for the ransomware’s deployment
The image below outlines all supported options of the ransomware. Each option necessitates an access token for usage, without it, the program remains inoperable
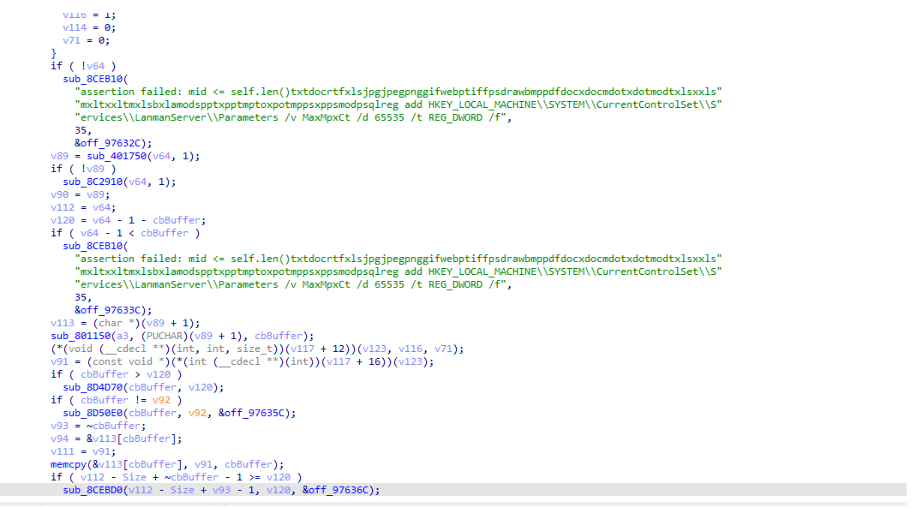
The ransomware modifies the registry to increase allowed requests, enhancing its lateral movement capabilities across more devices, this is achieved by adjusting the ‘MaxMpxCt‘ setting located at:
‘HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\LanmanServer\Parameters‘, set to 65535, using the force (/f) flag.
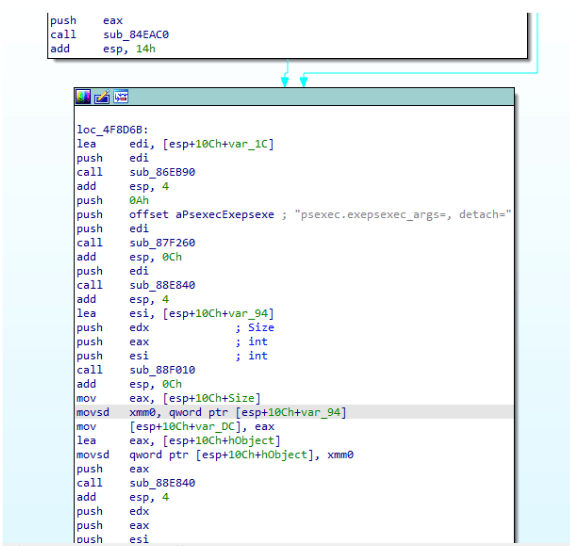
After increasing the number of permitted requests, the ransomware propagates across the network using the PsExec tool
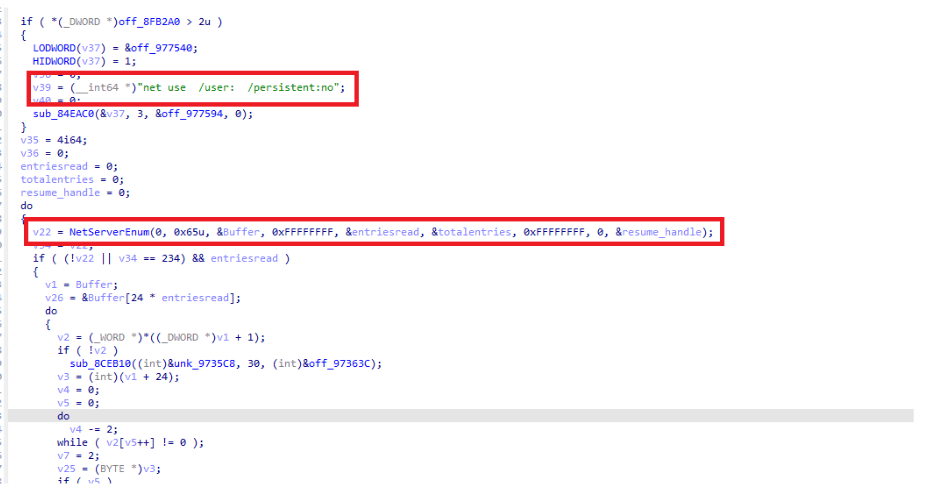
also it uses ‘NetServerEnum‘ api with ‘servertype‘ set to ‘0xFFFFFFFF‘, indicating an intent to retrieve all servers , then it try to connect to network shares on order to spread itself
The ransomware abuse the ‘wevtutil.exe‘ executable to erase all event logs, complicating the task of incident response team
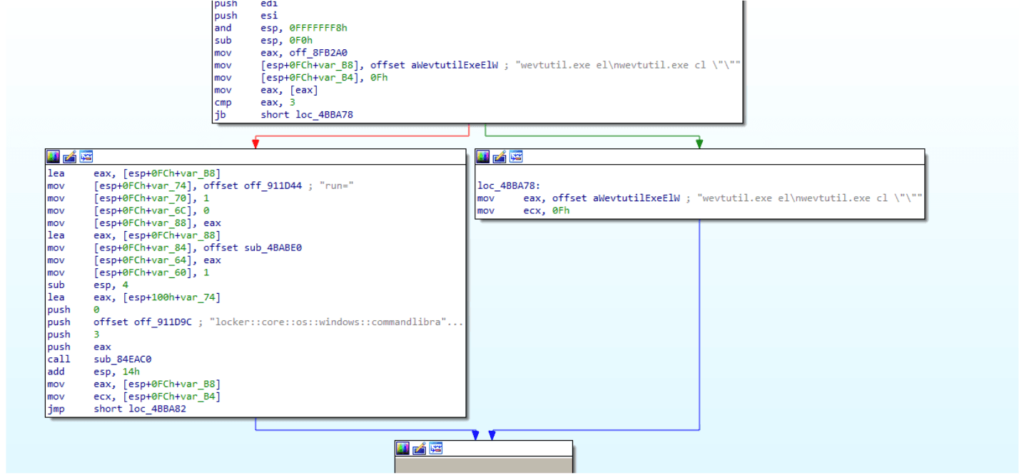
The ransomware note contains random characters, which are decrypted at runtime once the access token is provided, and written into a file called RECOVER-${EXTENSION}-FILES.txt ,This suggests that the extension name is generated for each target
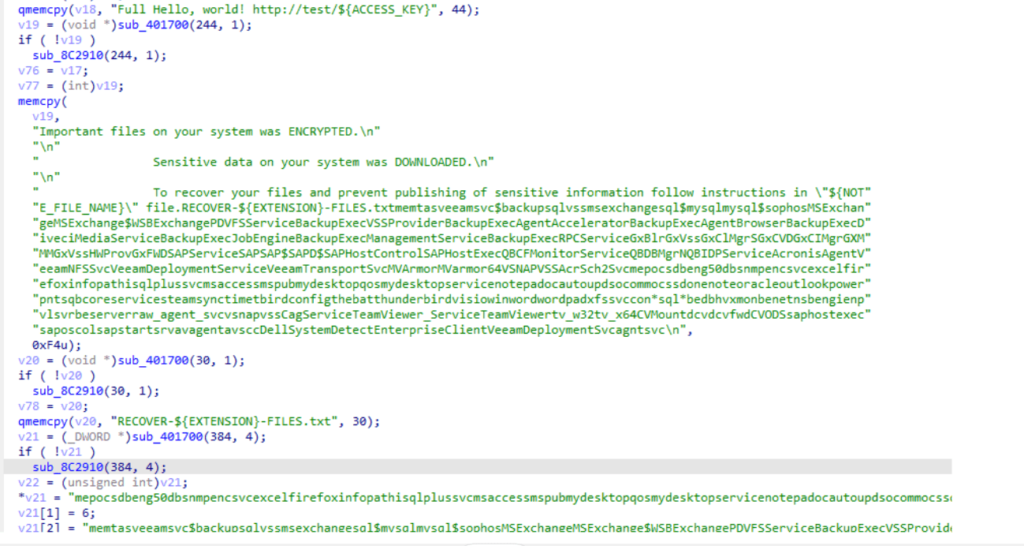
The ransomware note, after being decrypted at runtime, contains the file extension of the encrypted files, details about the stolen data, and instructions to contact the threat actor
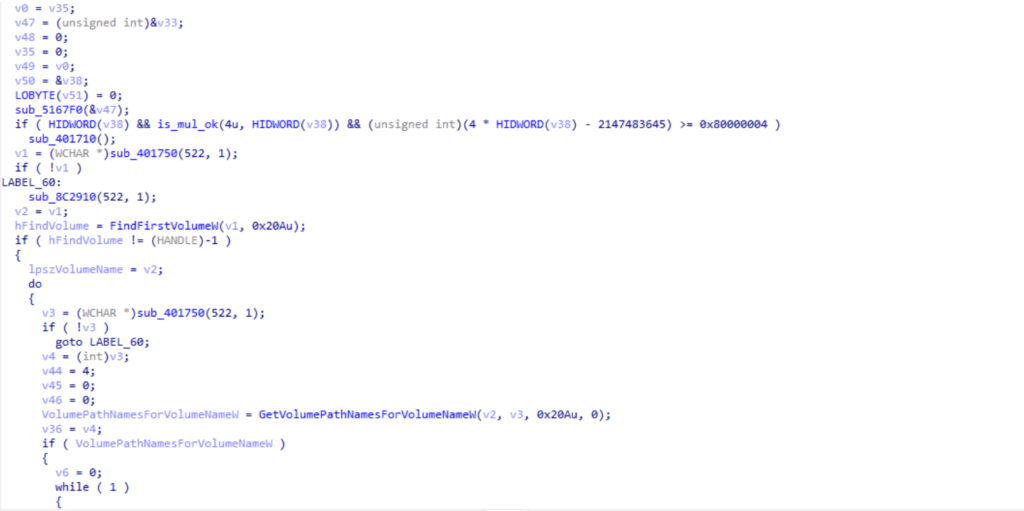
in the encryption phase the ransomware loop thourgh all volums then thourg all files with specific extension then start encrypting them , the encryption algorithm the ransomware support chacha and AES algorithms
According to their own RaaS�advertisements, BlackCat ransomware can be configured to use several
different encryption modes:
-
Full file encryption – the strongest but slowest encryption method.
-
Fast encryption – the opposite of full – sacrifices strength for speed as it only encrypts the first N
megabytes.
-
DotPattern encryption – favors speed but is still somewhat strong encryption by encrypting N
megabytes through M step.
-
SmartPattern encryption – the most optimal mode in terms of speed/strength ratio; encrypts N
megabytes in percentage steps (default: 10 megabytes every 10% of the file starting from the
header).
-
Auto– The encryption speed/strength can change depending on the type and size of the file,the choice will be optimized for both speed and security.
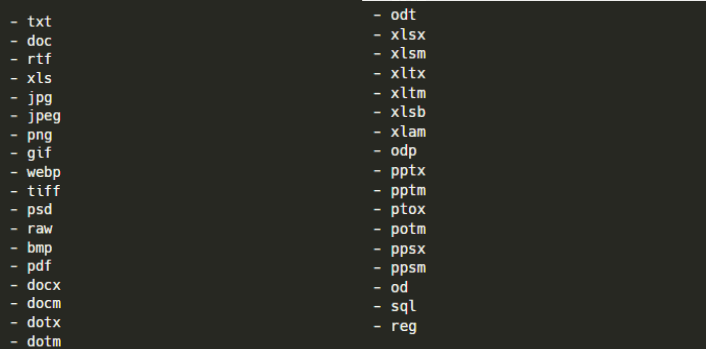
Targeted file extensions :
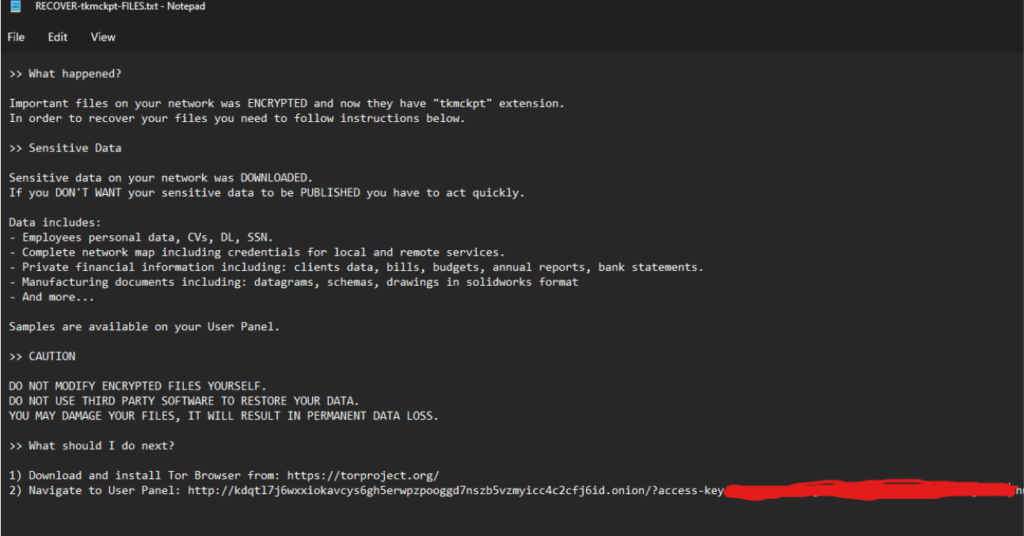
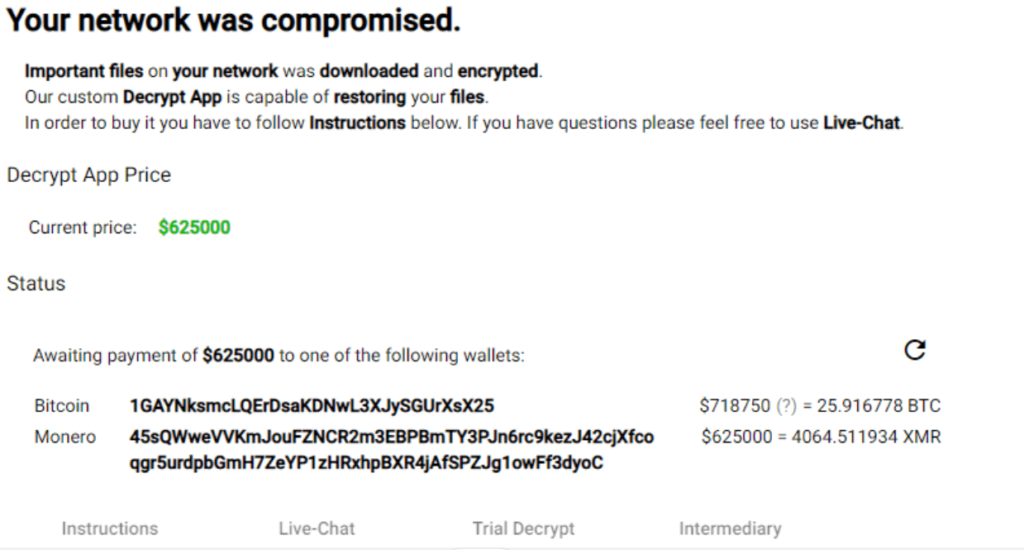
The threat actor offer a decryption program priced at $625,000. This application is allegedly capable of restoring the encrypted file, Payment instructions are provided with the option to use live-chat for queries. The current status shows the ransom amount awaiting payment in either Bitcoin or Monero cryptocurrencies , The equivalent of the ransom in Bitcoin is 25.794933 BTC, and in Monero, it is 4082.032526 XMR.
Ransomwre IOCs
-
C:\\Users\\Public\\All Usersdeploy_note_and_image_for_all_users=
-
–no-prop-servers–propagatedpropagate::server=
-
drag-and-drop-target.bat
-
Important files on your system was ENCRYPTED
MITRE ATT&CK Techniques
| Technique | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| TA0001 Initial Access | Exploit Public-Facing Application | ProxyShell vulnerabilities |
| T1133 External Remote Services | External Remote Services | Insecure RDP and VPNs |
| TA0006 Credential Access | OS Credential Dumping: LSASS Memory | procdump, comsvcs.dll |
| T1552 Unsecured Credentials | Unsecured Credentials | NirSoft utilities |
| TA0040 Impact | Data Encrypted for Impact, Service Stop, Inhibit System Recovery, Data Destruction | Encrypts files, stops services, deletes Windows Volume Shadow Copies |
| TA0003 Persistence | Server Software Component, Valid Accounts | ProxyShell exploits, legitimate accounts |
| TA0008 Lateral Movement | Remote Services: RDP, SMB, SSH, Lateral Tool Transfer | PsExec utility |
| TA0011 Command and Control | Command and Control | C2 |
| TA0004 Privilege Escalation | Valid Accounts, Abuse Elevation Control Mechanism, Access Token Manipulation | Bypass UAC, Create Process with Token |
| TA0005 Defense Evasion | Exploit Public-Facing Application, External Remote Services | ProxyShell vulnerabilities, Insecure RDP and VPNs |